35 Amazing Goal Setting Statistics You Should Know (2025)
Goal setting statistics and data give you clarity and step-by-step actions to achieve staggering growth.
In the year 2021, I achieved many of the goals I set. I was proud of how much my life changed. In the year, 2022. Not so much. Some goals worked out, but many didn’t. And I sat, frustrated, and unsure why.
You’ll find clear answers with these goals setting facts!

What are the top 5 facts about goal setting?
First, the most interesting, stunning, and beneficial data is as follows:
Would you like to save this idea?
1. Setting goals that are challenging but achievable lead to 90% better performance. (Psychological Bulletin)
2. Goals change the way we view the world. People with consistent goal-setting practices view the world in a more positive light and view challenges or failures as temporary setbacks rather than personal shortcomings or character flaws.” (linkedin.com)
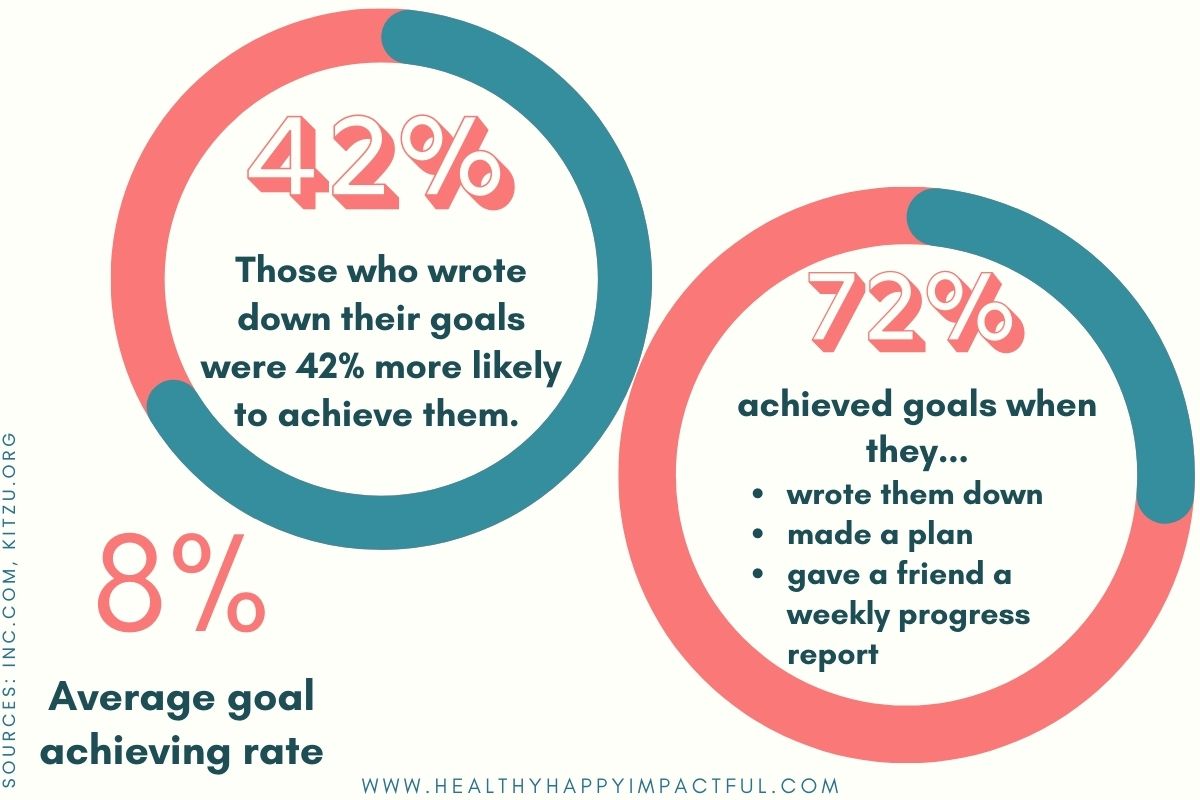
3. “People who wrote goals down, made a plan, and enlisted friends to help them by sending regular progress reports succeeded closer to 75% of the time.” (Dominican University study)
4. The more specific your goals are the more motivated you become, increasing your chances of achieving your goals. (Journal of Applied Psychology)
5. A learning goal leads to higher performance than a performance-based goal. (Button, Mathieu, & Zajac, 1995)
Great Research on Goal-Setting And Success

1. 80% of people do NOT set goals for themselves. (reliableplant.com)
2. Of the 20% of people who set goals, 70% of them do not achieve their goals. (reliableplant.com)
3. Goals change our brain. The brain will actually rewire itself in order to achieve the goal image. (linkedin.com)
4. Goals change the way we view the world. People with consistent goal-setting practices view the world in a more positive light and view challenges or failures as temporary setbacks rather than personal shortcomings or character flaws.”(linkedin.com)

5. Setting goals that are challenging but achievable lead to 90% better performance. (Locke, E. A., Shaw, K. N., Saari, L. M., & Latham, G. P. (1981). Goal setting and task performance: 1969–1980. Psychological Bulletin, 90(1), 125–152.)
6. Getting real with our abilities isn’t as scary as it once was. The more you set goals the less emotional and more tactical we process them. (linkedin.com)
Writing Down Goals Statistics
7. You are 3x more likely to achieve your goals if written down compared to having no written plan. (Harvard Business)
8. According to a study at the Dominican University of California, you are 42% more likely to achieve your goals if you write them down (Inc.com).
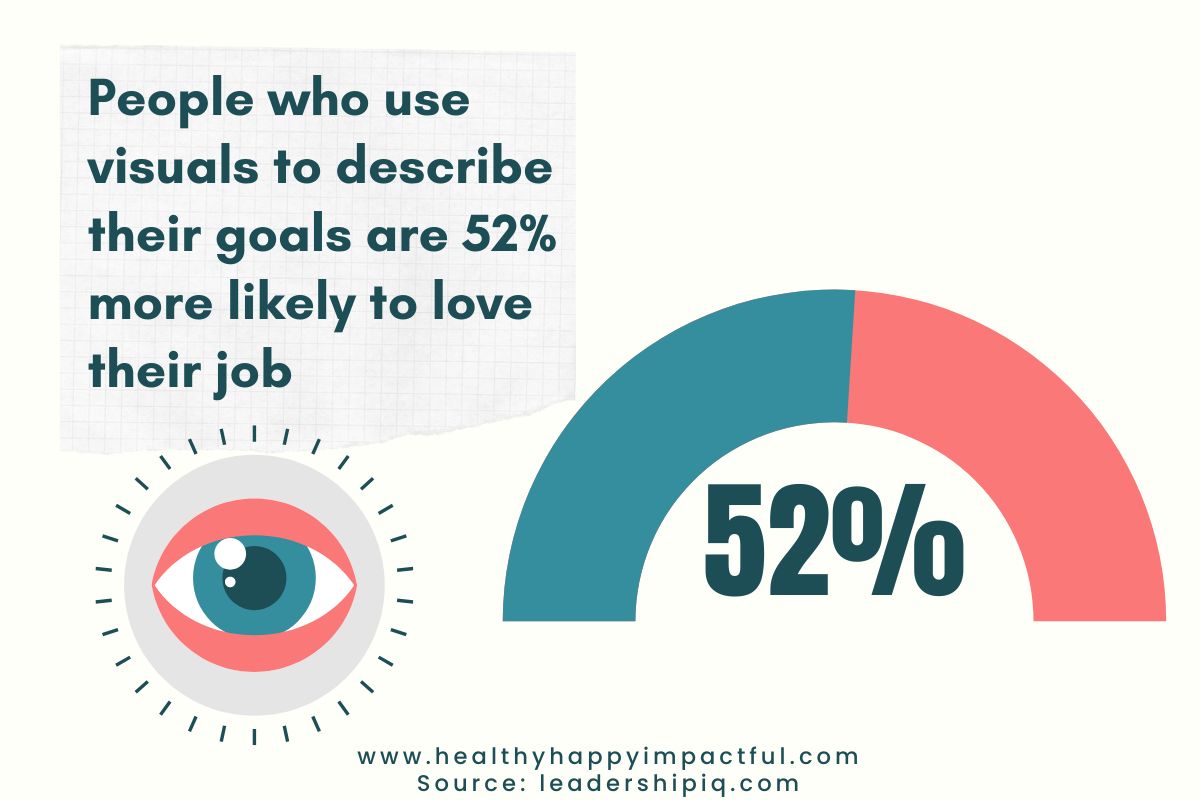
9. People who use visuals to describe their work goals are 52% more likely to love their job (leadershipiq.com)
Takeaway: Make it a daily habit to write and review your goals. And don’t be afraid to make it visual!
Statistics on Achieving Goals
Here you will learn the best strategies and tools to achieve your goals, according to science.
Involve Others For Even Better Results
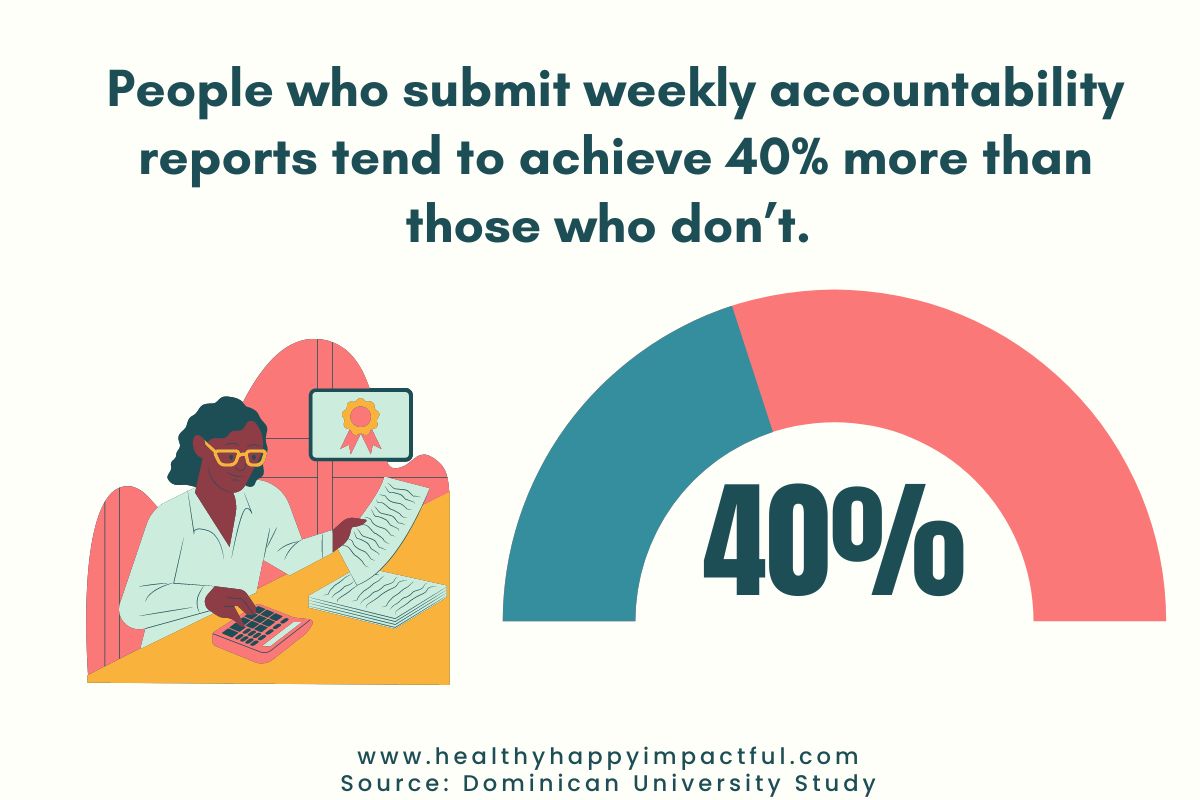
10. People who submit weekly accountability reports tend to achieve 40% more than those you don’t. (Dominican University)
11. In the same study at the Dominican University, people who wrote goals down, made a plan, and enlisted friends to help them by sending regular progress reports succeeded closer to 75% of the time.” (physcologytoday.com)
12. Receiving consistent feedback increases your chances in achieving your goals. (Becker, L. J. (1978). Joint effect of feedback and goal setting on performance: A field study of residential energy conservation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 63(4), 428–433.)
Takeaway: Pursuing goals with others, getting regular feedback, and finding an accountability partner are all great ways to help you succeed.
Be Specific Stats
13. The more specific your goals are the more motivated you become, increasing your chances of achieving your goals. (Arvey, R. D., Dewhirst, H. D., & Boling, J. C. (1976). Relationships between goal clarity, participation in goal setting, and personality characteristics on job satisfaction in a scientific organization. Journal of Applied Psychology, 61(1), 103–105.)
14. Specific, quantifiable goals lead to higher performance levels. (Locke & Latham, 2002).
15. Setting high and specific goals is linked to increased task performance, persistence, and motivation, compared to vague or easy goals (Locke, E. A., Shaw, K. N., Saari, L. M., & Latham, G. P. (1981). Goal setting and task performance: 1969–1980. Psychological Bulletin).
Takeaway: The more specific you can make your goals the better!
Get Into The Right Mindset Facts
16. Talking to yourself can help you stay on track with your goal. Your inner voice telling you to “keep going” is an effective method of controlling the impulse to give up. (physcologytoday.com)
17. People who have a greater understanding of their “why” are more likely to succeed in their goal. Yukl, Gary. Latham, Gary. (1978) Interrelationships among employee participation, individual differences, goal difficulty, goal acceptance, goal instrumentality, and performance. Personnel Psychology, 31(2), 305-325
18. Studies show that to increase the likelihood of achieving a goal, consider the effort needed when deciding what to do, and then remember to focus on the rewards once the time comes to put the effort in. (Queen Mary University of London. “Psychologists discover secret to achieving goals.” ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 20 February 2020.)
19. You can be TOO motivated that it hinders your success. Over-motivation and stimulation can cause a flood of dopamine to affect your reward sensors. Mental focus and attention to detail are affected and can decrease your chances of achieving your goal. (physcologytoday.com)
Takeaway: Utilize positive self-talk and remember your why and the rewards you are looking forward to (try visualization to help).
Establish Time Frames
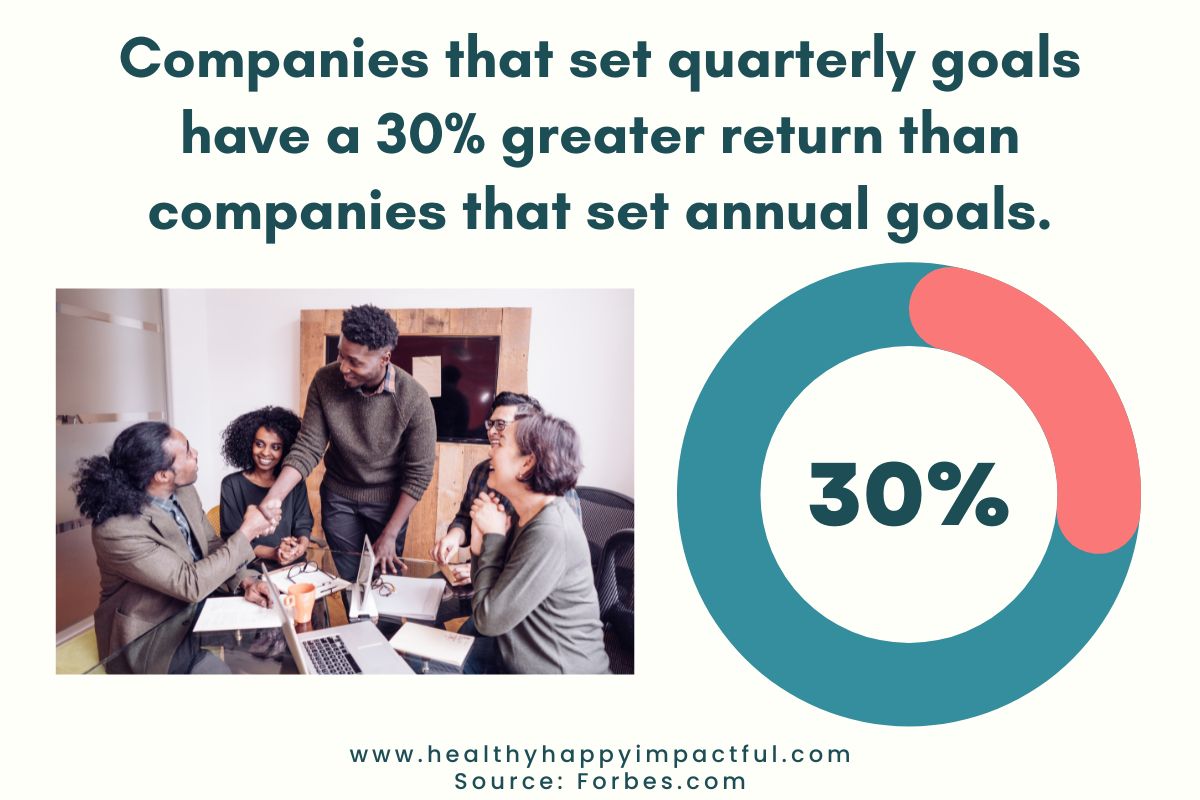
20. Companies that set quarterly goals have a 30% greater return than companies that set annual goals. (HR researcher and expert, Josh Bersin, forbes.com)
21. Deadlines improve the effectiveness of goals. (Lunenburg, Volume 15- 1, 2011 1 Goal-Setting Theory of Motivation)
Takeaway: Break longer goals into shorter deadlines.
Make It Physical
22. Clenching your left fist during high-pressure activity like achieving a physical performance goal can help you from “choking.” Studies indicate the right hemisphere of the brain is signaled which aids in automatic skill performance. (physcologytoday.com)
Type of Goals Matter Too (Goal Setting Statistics)
Go Big Data

23. Top executives are 91% more likely to enjoy getting out of their comfort zone in pursuit of their goals (leadershipiq.com)
24. People who set difficult goals are 34% more likely to love their jobs (leadershipiq.com)
25. The more challenging the goal, the more you’ll achieve. (Becker, L. J. (1978). Joint effect of feedback and goal setting on performance: A field study of residential energy conservation. Journal of Applied Psychology, 63(4), 428–433.)
Takeaway: Failing at a big audacious goal will still stretch you farther than achieving a realistic yet uninspiring one.
Focus on Learning, rather than performance
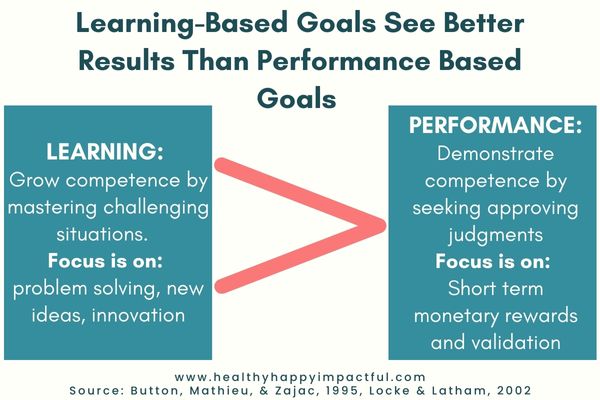
26. A learning goal leads to higher performance compared to a performance-based goal. (Button, Mathieu, & Zajac, 1995)
27. Combining goals with monetary rewards leads to easy-to-achieve goals, rather than more challenging and progress forward goals. (Locke & Latham, 2002).
28. Setting a goal that requires learning new skills is nearly 10 times more powerful at inspiring employees (leadershipiq.com)
More Goal Setting Statistics At Work
29. Goal setting in the workplace positively impacts employee engagement, increasing optimism and individual performance. (Medlin, Bobby, and Kenneth W. Green. “Enhancing performance through goal setting, engagement, and optimism.” Industrial management & data systems (2009).)
30. Entrepreneurs who set business goals will remain persistent in acting towards their business achievements. (Wu, S., Matthews and Dagher, G.K. (2007), “Need for achievement, business goals, and entrepreneurial persistence”, Management Research News, Vol. 30 No. 12, pp. 928-941.)
31. Specific goals help bring about other desirable organizational goals, such as reducing absenteeism, tardiness, and turnover (Locke & Latham, 2002).
Takeaway: Business goals provide many different benefits within the workplace.
New Year’s Resolutions (A.K.A. The Goals We Give Up On)
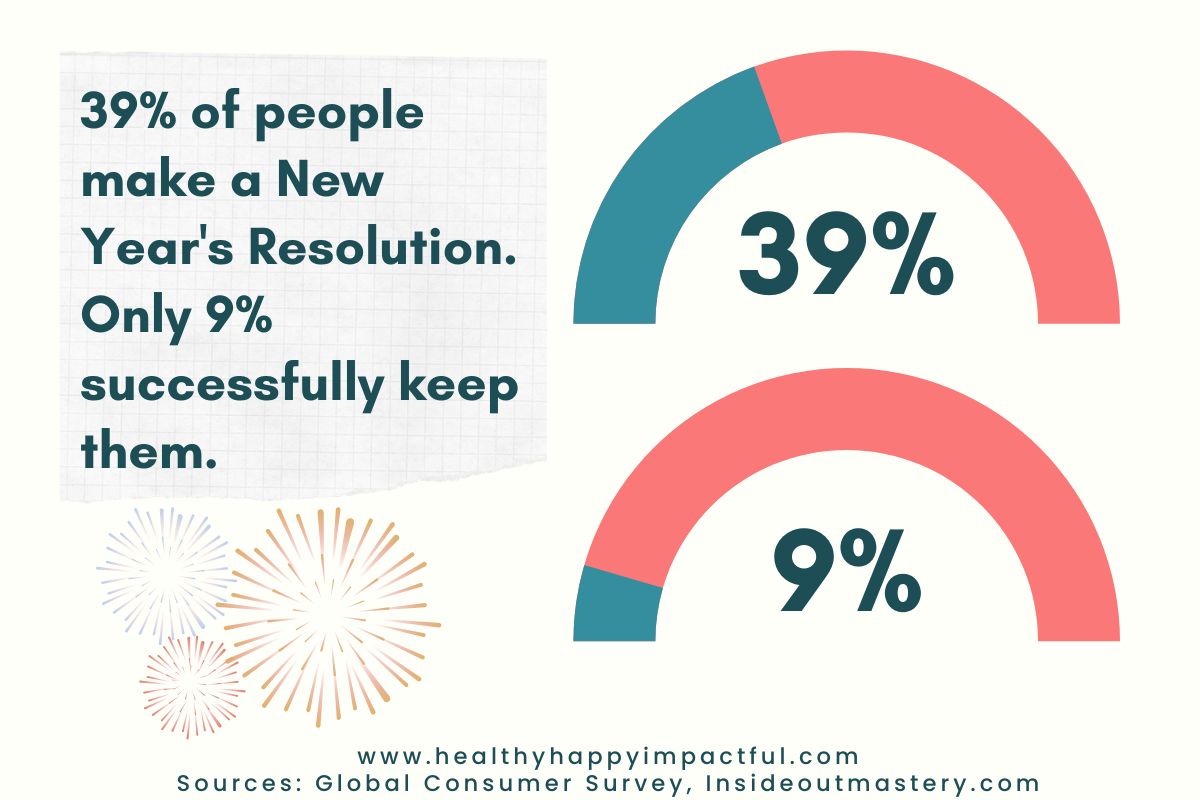
32. Only 39% of people will have a new year’s resolution. (Global Consumer Survey)
Of them, 9% successfully keep their New Year’s resolutions (insideoutmastery.com)
33. 46% of the people making a New Year’s resolution are successful in making positive changes towards their resolution (Norcross JC, Mrykalo MS, Blagys MD. Auld lang syne: success predictors, change processes, and self-reported outcomes of New Year’s resolvers and nonresolvers. J Clin Psychol. 2002)
Goal Setting Statistics Takeaway: New Year’s Resolutions aren’t easy to keep, but perhaps they still help you improve!
Quick Statistics on Giving Up
34. Giving up a goal takes a psychological and physical toll. The stress hormone cortisol is released and your blood pressure rises. (physcologytoday.com)
35. Statistics show that it takes 5 to 10 years of hard work on a project before it becomes incredibly successful. And yet most give up before they see the results of their effort (wealthygorilla.com)
Takeaway: When you most want to quit, keep going!
Goal Setting Statistics & My Varied Results

Overall, you’ll notice that the more you put into setting up your goals, the more you see out of them.
In 2021 (the year I succeeded often), I relied heavily on challenges and accountability from others. And it shows! My goals were also more learning based.
These stats also help me see that while I may not have achieved all of my goals in 2022, it’s ok. They were challenging and audacious, and I grew in the process, even if I’m not at the end result yet.
You can be sure that I’ll be writing my goals and engaging others more in 2023 though! What insights did you gain from these goal setting statistics? Leave a comment and let me know!
What’s Next?
Use our free habit and goal contract to keep more self-commitments!


Although not a statistic, I would add that those with higher emotional intelligence are more likely to achieve their goals.
These people are aware of what propels them forward and holds them back.
Motivation is higher, and their ability to manage the emotions influencing action is higher.
Consider building your emotional intelligence as a starting point, and then all the habits you wish to adopt will become much more manageable.